Multi-Casskop on Google Kubernetes Engine
Alexandre Guitton
Alexandre GuittonPre-requisites#
User should need :
- terraform version v0.12.7+
- kubectl version v1.13.3+
- kubectx & kubens
- Helm version v2.15.1+
- gcloud sdk version 272.0.0+
- A service account with enough rights (for this example :
editor) - Having a DNS zone in google cloud dns.
Setup GCP environment#
To setup the GCP environment we will use terraform provisionning, to instantiate the following infrastructure :
- 2 GKE clusters :
- First on europe-west1-b which will be the
master - Second on europe-west1-c which will be the
slave
- First on europe-west1-b which will be the
- Firewall rules to allow clusters to communicate
- External DNS on each cluster to expose cassandra nodes
- Casskop operator on each cluster to focus on multi-casskop usage
Environment setup#
Start to set variables needed for the instantiation :
Setup base infrastructure#
Master provisionning#
With the master provisionning, we will deploy firewall and Cloud dns configuration :
Slave provisionning#
Check installation#
Check master configuration#
Now we will check that everything is well deployed in the GKE master cluster :
Check slave configuration#
Now we will check that everything is well deployed in the GKE slave cluster :
Check DNS zone configuration#
Make a note of the nameservers that were assigned to your new zone :
Check Firewall configuration#
@TODO : rework firewall source
Check Storage Class#
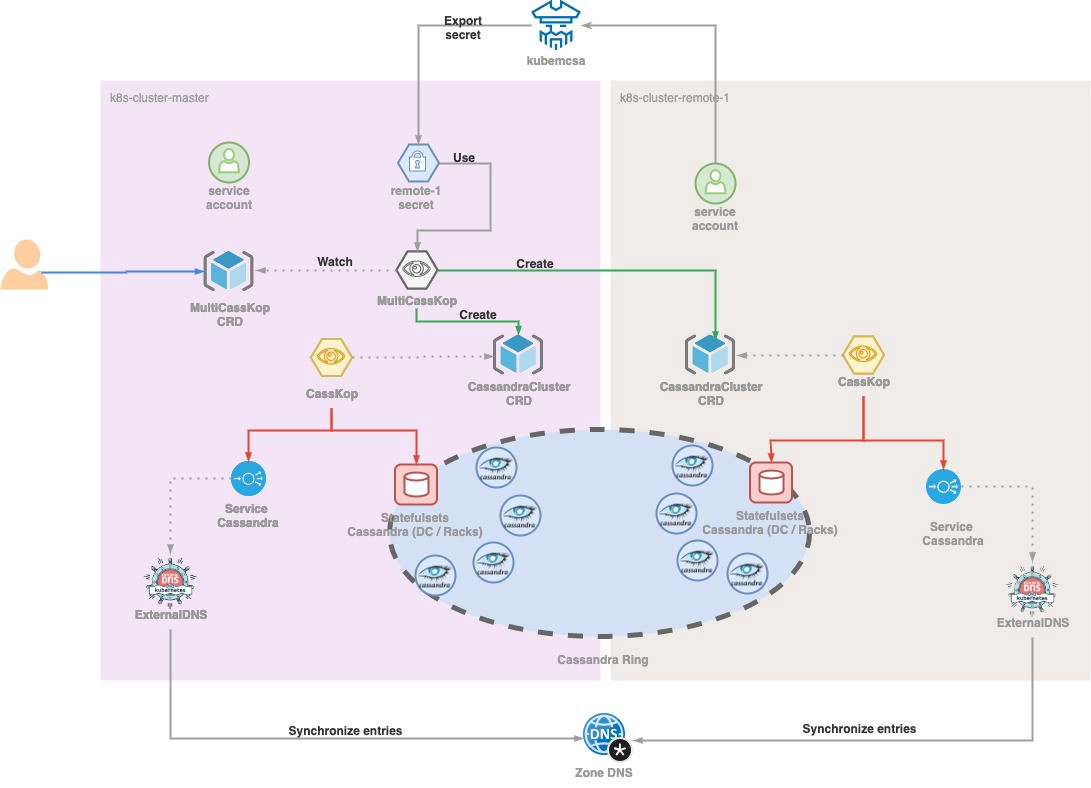
Multi casskop deployment#
Bootstrap API access to Slave from Master#
Multi-Casskop will be deployed in master cluster, change your kubectl context to point this cluster.
In order to allow Multi-CassKop controller to have access to slave from master, we are going to use kubemcsa from admiralty to be able to export secret from slave to master.
Install kubemcsa :
Generate secret for master :
Check that the secret is correctly created
Install Multi-CassKop#
@TODO : To correct once the watch object will be fixed
Add MultiCasskop crd on the slave cluster :
Deployment with Helm :
Create the MultiCasskop CRD#
Now we are ready to deploy a MultiCassKop CRD instance.
We will use the example in multi-casskop/config/samples/gke/multi-casskop-gke.yaml :
Check multi cluster installation#
We can see that each cluster has the required pods :
If we go in one of the created pods, we can see that nodetool see pods of both clusters :
Clean up everything#
If you have set the deleteCassandraCluster to true, then when deleting the MultiCassKop object, it will cascade the deletion of the CassandraCluster object in the targeted k8s clusters. Then each local CassKop will delete their Cassandra clusters (else skip this step)
Cleaning slave cluster#
Cleaning master cluster#
Before running the following command, you need to clean dns records set.